Executive Summary
The Swiss silicone sealants market for construction and industrial applications represents a mature yet dynamically evolving segment within the nation’s advanced manufacturing and building sectors. Characterized by stringent quality standards, a strong emphasis on sustainability, and a high-value industrial base, the market is navigating a complex landscape of technological innovation, regulatory shifts, and evolving end-user demands. This report provides a comprehensive 2026 analysis of the market’s current state, dissecting the intricate balance between established applications in glazing and facade engineering and emerging opportunities driven by energy efficiency mandates and advanced industrial manufacturing. The forecast horizon to 2035 is examined through the lens of these underlying drivers, offering a strategic perspective on the market’s trajectory without projecting specific volumetric figures.
Core demand remains fundamentally tethered to Switzerland’s robust construction activity, particularly in renovation and energy retrofit projects, as well as its world-class industrial sectors including precision machinery, pharmaceuticals, and clean technology. However, the market is increasingly segmented by performance specifications, with high-growth niches such as fire-resistant, structural glazing, and low-VOC formulations gaining prominence. The competitive landscape is defined by the presence of multinational chemical giants competing with specialized suppliers on the basis of technical service, product certification, and supply chain reliability, rather than price alone.
This analysis concludes that the Swiss market’s evolution towards 2035 will be less about volumetric expansion and more about value-driven specialization and product substitution. Success for industry participants will hinge on the ability to align R&D with regulatory trends like the Minergie standard, provide solutions for modular construction and building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV), and ensure seamless logistics within the Alpine geography. The subsequent sections provide a granular examination of the market’s structure, demand catalysts, supply mechanisms, trade flows, price determinants, and competitive dynamics that underpin this strategic outlook.
Market Overview
The Swiss market for construction and industrial silicone sealants is a high-value, specification-intensive arena within the broader European adhesives and sealants industry. Its development is intrinsically linked to the country’s economic pillars: a stable, innovation-driven construction sector and a diverse, export-oriented industrial base. The market is distinguished by an exceptionally high bar for product performance, durability, and environmental compliance, reflecting Switzerland’s rigorous building codes, environmental consciousness, and the technical demands of its industrial output. As of the 2026 analysis point, the market has fully internalized EU-derived regulations on chemical safety and VOC emissions, which act as a baseline, with local standards often pushing requirements further.
Market maturity implies that growth is not primarily volume-led but is instead driven by the penetration of advanced, multi-functional sealant solutions that offer superior longevity, safety features, or sustainability credentials. The replacement cycle in the vast stock of existing buildings, particularly from construction booms of the late 20th century, provides a steady, predictable demand stream for maintenance and renovation. Simultaneously, new construction, especially in urban centers and infrastructure projects, integrates higher-performance sealants from the outset, elevating the average value per unit.
The industrial segment, while smaller in volume compared to construction, commands a significant premium and is critical for technological innovation. Applications in electrical and electronics encapsulation, aerospace component assembly, and medical device manufacturing require sealants with extreme purity, specific thermal or conductive properties, and compliance with exacting industry-specific standards. This bifurcation between large-volume construction applications and high-margin, low-volume industrial specialties defines the market’s dual character and necessitates distinct strategic approaches from suppliers.
Demand Drivers and End-Use
Demand for silicone sealants in Switzerland is propelled by a confluence of regulatory, economic, and technological factors. The primary and most stable driver is the nation’s construction and renovation activity. Switzerland’s building stock is aging, with a significant portion requiring energy efficiency upgrades to meet federal climate targets and cantonal regulations. Silicone sealants are critical enablers in window replacement, facade insulation system installation, and the sealing of building envelopes to achieve Minergie and similar standards. This creates a resilient, non-cyclical demand base less susceptible to short-term economic fluctuations than pure new-build construction.
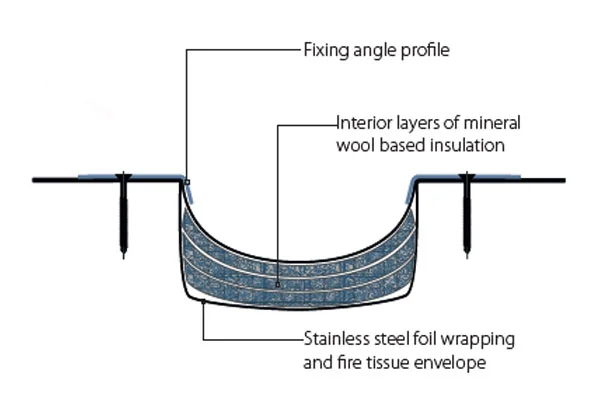
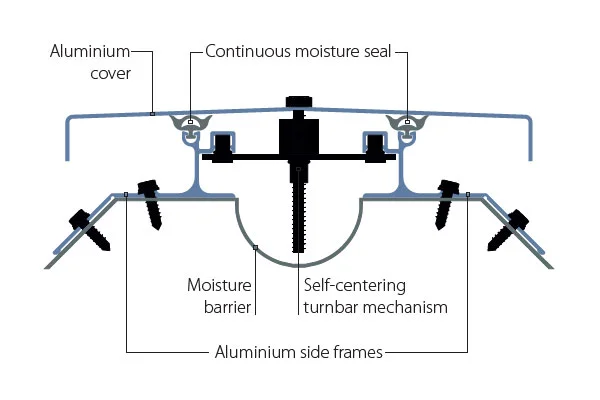
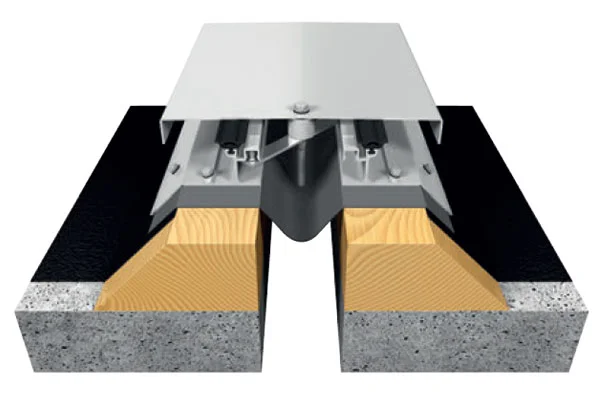
Beyond renovation, specific construction trends are shaping demand patterns. The growth of prefabricated and modular construction methods places a premium on sealants that accommodate panel movement and ensure long-term weatherproofing at junction points. The integration of solar technology into buildings (BIPV) requires specialized sealants that protect photovoltaic components while maintaining structural integrity and aesthetics. Furthermore, stringent fire safety regulations in public buildings and high-rises are accelerating the adoption of certified fire-stop and fire-resistant silicone sealants, a high-value niche.
In the industrial domain, demand is more closely tied to the performance of Switzerland’s flagship sectors. The precision machinery, electrical engineering, and metalworking industries utilize sealants for bonding, sealing, and protecting sensitive components from moisture, dust, and vibration. The thriving pharmaceutical and medical technology sectors demand ultra-pure, biocompatible, and easily sterilizable silicone formulations for equipment and device assembly. The transport sector, particularly railway and aerospace subcontracting, requires sealants that withstand extreme temperature cycles and mechanical stress. Each of these segments drives innovation towards more specialized product formulations.
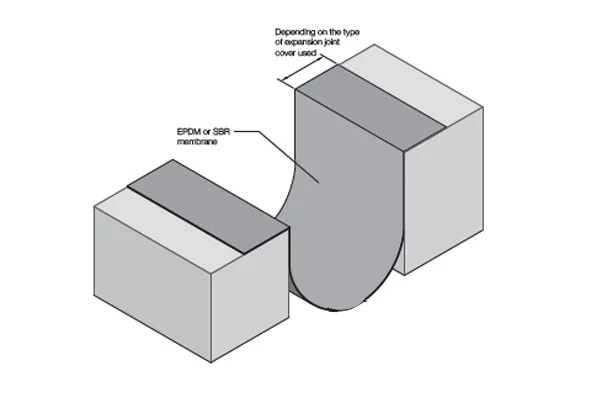
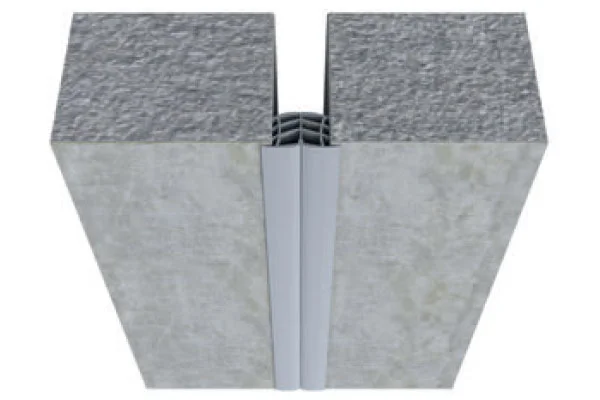
- Key Construction End-Uses: Structural glazing and curtain walls; window and door perimeter sealing; expansion joint sealing in facades and concrete structures; sanitary and wet room sealing; fire protection systems.
- Key Industrial End-Uses: Gasketing and encapsulation in electrical/electronic devices; bonding and sealing in precision instrument assembly; component sealing in automotive and aerospace; sanitary sealing in food and pharmaceutical processing equipment.
Supply and Production
The supply landscape for silicone sealants in Switzerland is predominantly characterized by imports, with domestic production capacity being limited and focused on specific, high-value formulations or final packaging and compounding operations. The core raw materials for silicone polymers—primarily silicon metal and various methyl chlorosilanes—are not produced domestically at scale. Therefore, the supply chain is deeply integrated into the European and global silicones network, with multinational chemical companies often sourcing intermediates from their large integrated production sites in Germany, France, or other global hubs.
Local Swiss production, where it exists, typically involves the compounding of imported silicone bases with additives, catalysts, pigments, and fillers to create finished sealant products tailored to local market specifications. This allows for flexibility in meeting custom color matching, specific performance profiles requested by Swiss architects or engineers, and rapid response to local demand. Some specialized manufacturers serving the pharmaceutical or electronics industries may maintain clean-room production facilities for ultra-high-purity grades. However, the vast majority of volume consumed in standard construction applications is supplied via imports of finished goods from production plants located across Europe.
The logistics of supply are complicated by Switzerland’s landlocked Alpine geography and its complex relationship with the European Union’s regulatory and customs framework. Efficient supply relies on well-established transport corridors through Germany, France, Italy, and Austria. Suppliers and distributors must maintain strategic stockholding within Switzerland to ensure just-in-time delivery to construction sites and industrial plants, mitigating potential border delays. This necessity for local warehousing and technical sales support elevates the importance of a strong physical and service-oriented presence within the country, creating a barrier to entry for purely import-focused distributors without local value-added services.
Trade and Logistics
Switzerland’s trade in silicone sealants is defined by a consistent structural trade deficit, reflecting its status as a net importer to satisfy robust domestic demand. The country’s exports of sealants are minimal and typically consist of re-exports of specialized products or niche shipments tied to Swiss machinery or pre-fabricated building components sent abroad. The import flow is the critical lifeline for the market, with European Union member states constituting the overwhelming majority of sources. Germany, as Europe’s industrial heartland and home to major chemical conglomerates, is typically the largest single source of imports, followed by other neighboring industrial nations like France, Italy, and Austria.
The import portfolio is diverse, ranging from bulk shipments of standard cartridge-ready sealants for the construction trade to palletized goods of industrial-grade products in smaller, specialized packaging. The trade channels are equally varied, involving direct sales from multinational manufacturers to large construction groups or industrial OEMs, as well as multi-tiered distribution through national and regional wholesale distributors specializing in construction chemicals, paints, and coatings. These distributors play a crucial role in reaching the fragmented base of small and medium-sized construction firms and trade professionals (glaziers, facade builders, sanitarians).
Logistical efficiency is paramount. The combination of just-in-time construction schedules and the need to minimize on-site storage drives a requirement for reliable, frequent deliveries. Distributors operate centralized warehouses and regional depots to ensure coverage across Switzerland’s major economic regions (Zurich, Lake Geneva, Mittelland). The cross-border transport is highly professionalized, but remains subject to the overarching framework of Swiss-EU bilateral agreements, requiring meticulous customs documentation and compliance with both Swiss and EU chemical safety regulations (CLP, REACH). This regulatory duality adds a layer of complexity and cost to the import process that is factored into market pricing.
Price Dynamics
Price formation in the Swiss silicone sealants market is influenced by a multifaceted set of factors beyond simple supply-demand mechanics. Firstly, input cost volatility plays a significant role. The prices of key raw materials—silicone polymers (elastomers), fillers, and additives—are subject to global petrochemical and energy market fluctuations. As these upstream costs are denominated in currencies like the US dollar or euro, exchange rate movements between the Swiss franc (CHF) and these currencies directly impact the landed cost of imported materials and finished goods.
Secondly, the value-added structure within Switzerland imposes its own costs. The expenses associated with compliance with stringent national building codes (e.g., SIA norms) and environmental regulations, including costs for testing, certification (e.g., UEAtc, ISO), and eco-labeling, are embedded in final product prices. Furthermore, the high costs of skilled labor for technical sales support, distribution logistics in an expensive operating environment, and local warehousing contribute to a price premium compared to less regulated markets. This results in a market where competition is often based on technical service, brand reputation for reliability, and product performance rather than being purely price-driven.
Finally, end-user segmentation creates distinct price tiers. Standard construction-grade neutral-cure acetoxy or alkoxy sealants sold through retail channels are highly price-competitive. In contrast, specialized products—such as structural glazing sealants, high-movement facade joint sealants, fire-resistant systems, or medical-grade adhesives—command substantial price premiums due to their advanced formulations, extensive testing requirements, and the critical nature of their applications. In these segments, buyers are less price-sensitive and more focused on total cost of ownership, including installation reliability and long-term durability, which justifies the higher initial investment.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive arena in Switzerland is dominated by the European subsidiaries of global chemical and silicone giants, who leverage their integrated supply chains, extensive R&D capabilities, and global brand recognition. These players compete across the entire spectrum, from construction to high-tech industry, offering comprehensive product portfolios. Their strength lies in their ability to provide consistent quality at scale, invest in technical marketing and specification influence with architects and engineers, and offer global key account management for multinational construction firms and industrial OEMs operating in Switzerland.
Alongside these multinationals, a layer of strong, often regionally-focused, European specialty chemical companies and independent sealant manufacturers hold significant market share, particularly in specific construction niches or industrial specialties. These competitors often compete on deep technical expertise in a particular application, superior customer service, flexibility in custom formulation, or more agile logistics. They may also partner with or supply private-label products to large Swiss construction wholesalers and distributors, who themselves are powerful channel players with their own brand presence and direct customer relationships.
The distribution network is a critical battleground. Competition occurs not only among manufacturers but also among distributors vying for partnerships with the most reputable suppliers and for contracts with large purchasing cooperatives of construction firms. The landscape is consolidated at the top but features a long tail of smaller, specialized distributors. Key competitive strategies observed in the market include a strong focus on sustainability marketing (low VOC, recyclability), digital tools for product selection and specification, and providing extensive on-site technical support and training for applicators to ensure correct usage and minimize warranty claims.
- Representative Multinational Players: Companies like Sika (headquartered in Switzerland, providing a strong home-field advantage), Henkel, 3M, Arkema (Bostik), and Dow are typically key participants.
- Competitive Strategies: Product differentiation via certification and labeling; intensive technical support and training; development of sustainable product lines; strategic partnerships with distributors and system suppliers.
Methodology and Data Notes
This market analysis is built upon a multi-faceted research methodology designed to triangulate data and provide a holistic, accurate view of the Swiss silicone sealants sector. The foundation consists of the systematic analysis of official trade statistics, which provide a quantitative backbone for understanding import volumes, values, and geographic trade patterns. These hard data are supplemented by the review of industry publications, company annual reports, technical datasheets, and regulatory announcements from bodies such as the Swiss Federal Office for the Environment (FOEN) and the Swiss Society of Engineers and Architects (SIA).
Furthermore, the analysis integrates insights from targeted interviews and surveys conducted across the value chain. This qualitative component involves discussions with industry stakeholders including product managers at manufacturing firms, sales directors at distribution companies, procurement specialists within construction conglomerates, and specifying engineers in consulting firms. This primary research is crucial for interpreting quantitative data, understanding pricing mechanisms, competitive behaviors, and identifying emerging trends that may not yet be fully visible in statistical datasets.
All market size estimations, growth rate inferences, and market share assessments presented are the result of this analytical synthesis. It is important to note that the Swiss market, due to its high degree of specialization and the presence of direct sales from manufacturers to large end-users, presents challenges for precise volumetric measurement. Therefore, the analysis places emphasis on directional trends, structural shifts, and qualitative dynamics rather than claiming unwarranted precision. The forecast perspective to 2035 is derived from modeling the impact of identified demand drivers, regulatory roadmaps, and macroeconomic indicators on the market’s established structure.
Outlook and Implications
The trajectory of the Swiss silicone sealants market towards 2035 will be shaped by the continued interplay of stringent regulation, technological advancement, and sustainability imperatives. Volume growth is expected to remain modest, closely correlated with overall construction investment and industrial output indices. However, the market’s value evolution will be more dynamic, driven by the ongoing shift towards premium, multi-functional products. Regulatory pressure for higher building energy efficiency and improved fire safety will persist as non-negotiable demand catalysts, ensuring steady replacement and upgrade cycles. The trend towards prefabrication and digitalization in construction (BIM) will further integrate sealant specification into early design phases, favoring suppliers with strong technical data and digital tools.
For industry participants, several strategic implications are clear. Manufacturers must continue to invest in R&D focused on sustainable chemistry, including bio-based or enhanced recyclability of silicone materials, to align with circular economy principles. The ability to offer “system solutions”—combining sealants with complementary tapes, adhesives, and installation methodologies—will be a key differentiator. For distributors, value creation will increasingly depend on logistics excellence, inventory management of a wider portfolio of specialized products, and providing value-added services like on-site technical troubleshooting and waste take-back programs.
Market entrants face significant barriers rooted in the need for local certification, established brand trust, and the requirement for a robust technical service infrastructure. However, opportunities exist for specialists in ultra-niche industrial applications or in developing novel sealant chemistries that address specific environmental or performance gaps. Ultimately, the Swiss market to 2035 will reward those players who can successfully navigate its complex, high-standard environment by combining global innovation capabilities with deep local market understanding, reliable supply chain execution, and an unwavering commitment to quality and sustainability. This report provides the foundational analysis required to formulate and execute such strategies in this sophisticated and demanding marketplace.
Source: IndexBox Platform