Executive Summary
The European expansion joints market represents a critical, if often understated, component of the continent’s industrial and civil infrastructure. As of the 2026 analysis, the market is characterized by steady demand driven by aging asset renewal, stringent regulatory frameworks, and investments in sustainable energy and transportation networks. The market’s trajectory is not uniform, with significant regional variations in growth rates and demand intensity reflecting differing economic conditions and investment priorities across Western, Central, and Eastern Europe.
This report provides a comprehensive examination of the market from 2026 through the forecast horizon to 2035. It dissects the complex interplay between mature, replacement-driven sectors and emerging opportunities in green technology and modernized infrastructure. The analysis extends beyond simple volume metrics to explore supply chain dynamics, price sensitivity to raw material inputs, and the strategic positioning of key market participants.
The outlook to 2035 suggests a market in transition, where technological innovation in materials and smart monitoring systems will increasingly dictate competitive advantage. While macroeconomic cycles will influence short-term capital expenditure, the foundational drivers of safety, regulatory compliance, and infrastructure resilience ensure the market’s long-term stability and gradual evolution.
Market Overview
The European expansion joints market is a mature yet essential industry, integral to the longevity and safety of a wide array of structures and systems. These components are engineered to absorb thermal expansion, contraction, vibration, and settlement in constructed assets, preventing structural damage. The market’s size and stability are directly tied to the scale and condition of Europe’s built environment, encompassing decades-old infrastructure and new, ambitious projects.
Geographically, demand is heavily concentrated in Western Europe, which hosts the largest stock of industrial plants, commercial buildings, and advanced transportation networks requiring maintenance and upgrades. The Benelux countries, Germany, France, Italy, and the United Kingdom have traditionally been the core demand centers. However, Central and Eastern Europe are emerging as areas of growing importance, fueled by EU cohesion funds and national initiatives aimed at modernizing infrastructure and industrial bases to meet Western standards.
The market is segmented by product type, with key categories including metallic expansion joints (often used in high-pressure, high-temperature industrial applications), rubber expansion joints (common in piping systems for vibration dampening), and other specialized types for bridges and large-scale civil structures. Each segment responds to distinct demand drivers, regulatory codes, and competitive pressures, creating a multifaceted market landscape.
From a value chain perspective, the market involves raw material suppliers (steel, rubber, fluoropolymers), manufacturers and fabricators of the joints, a network of engineering and distribution partners, and finally, the end-users across various industries. The performance and cost of raw materials, particularly specialty alloys and elastomers, are a primary determinant of product pricing and manufacturer margins, creating a direct link between global commodity markets and the finished goods market in Europe.
Demand Drivers and End-Use
Demand for expansion joints in Europe is not generated by a single sector but is diversified across multiple, sometimes cyclical, end-use industries. This diversification provides a degree of stability, as downturns in one sector may be offset by growth in another. The primary demand is derived from the need for maintenance, safety upgrades, and compliance with evolving regulations, rather than purely from new construction.
The chemical and petrochemical industry constitutes a major end-use segment. Complex piping networks in refineries, chemical plants, and LNG terminals are subject to extreme thermal and pressure cycles, making high-performance metallic expansion joints critical for operational safety and preventing costly downtime. Environmental regulations pushing for reduced fugitive emissions are driving upgrades to sealing technologies within these joints.
Energy generation and distribution is another pivotal sector. This includes both traditional power plants (coal, gas, nuclear) and the rapidly expanding renewable energy infrastructure. Expansion joints are essential in power plant piping, flue gas desulfurization systems, and district heating networks. The transition to renewables creates specific demand in biomass plants, waste-to-energy facilities, and the piping systems for concentrated solar power (CSP) plants.
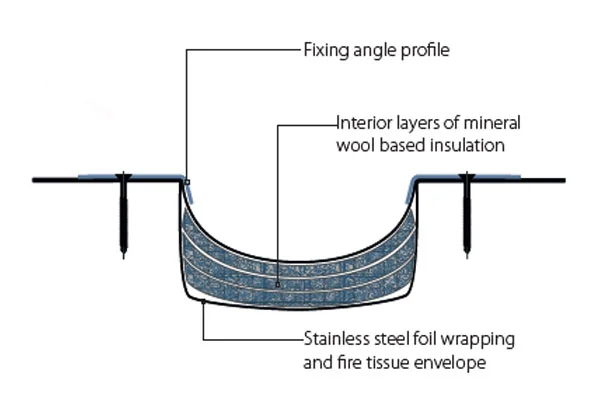
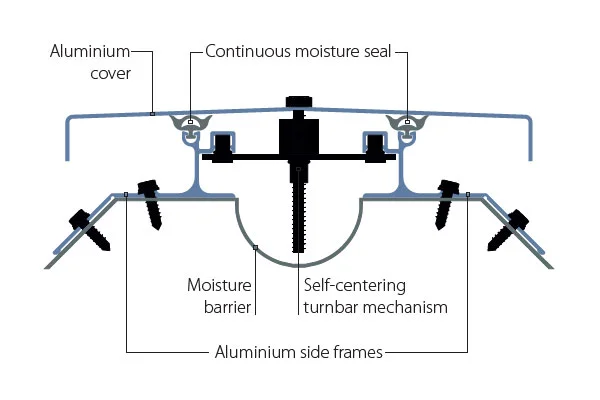
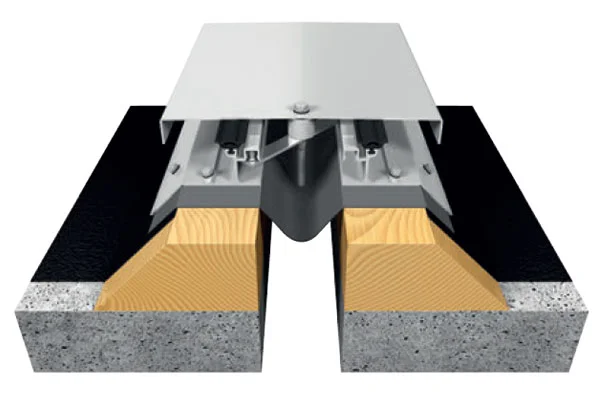
Transportation infrastructure represents a significant and highly visible application area, particularly for large-scale rubber and modular bridge expansion joints. The maintenance and expansion of Europe’s road and rail networks, including bridges, tunnels, and airport runways, require joints that can handle dynamic loads, weather extremes, and decades of service life. Investment in high-speed rail and the renewal of aging bridge stock are consistent demand sources.
Other important end-use sectors include water and wastewater treatment, where joints manage movement in large-diameter pipes and tanks; commercial and industrial construction for HVAC systems; and shipbuilding, where they are used in engine exhaust systems and piping. The common thread across all sectors is the non-discretionary nature of the product for system integrity and safety, underpinning a resilient baseline demand.
Supply and Production
The supply landscape for expansion joints in Europe is bifurcated, featuring a mix of large, multinational engineering conglomerates and a layer of specialized, often regionally-focused, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The large players typically offer a broad portfolio of flow control and piping components, with expansion joints as one product line among many, leveraging extensive R&D capabilities and global sales networks.
In contrast, the SME segment often competes on deep technical expertise in niche applications, customized engineering solutions, and responsive customer service. These companies may specialize in a particular material type (e.g., high-nickel alloys for corrosive environments) or a specific end-market (e.g., bridge joints). The production process is characterized by a blend of standardized component manufacturing and project-specific fabrication and assembly, making it relatively resistant to full automation and offshoring.
Production capacity in Europe is geographically aligned with historical industrial centers. Key manufacturing clusters are found in Germany, Italy, the United Kingdom, and the Benelux region, benefiting from proximity to skilled labor, advanced metallurgical and polymer industries, and major end-user customers. The trend towards “just-in-time” delivery and the need for rapid technical support for critical installations further incentivizes regional production.
Supply chain robustness has become a paramount concern following recent global disruptions. Manufacturers are scrutinizing their supplier base for critical raw materials like specific steel grades and specialty elastomers, with some seeking to nearshore or diversify sources to mitigate risk. This focus on supply chain resilience, coupled with rising energy and labor costs in Europe, is placing pressure on production economics and influencing strategic decisions about capacity location.
Trade and Logistics
International trade plays a significant role in the European expansion joints market, though its nature varies by product segment. The region is both a major exporter of high-value, engineered expansion joint systems and an importer of more standardized, cost-competitive products. The trade balance is generally positive for European manufacturers in high-specification segments, reflecting their technological edge.
Intra-European trade is fluid, supported by the EU’s single market and harmonized technical standards. German and Italian manufacturers, in particular, are key exporters to other European nations. Extra-European trade sees competition from Asian manufacturers, especially in lower-complexity rubber and standard metallic joints, where price competition is intense. Conversely, European firms export sophisticated solutions globally, particularly to the Middle East, Asia, and North America for large-scale industrial and energy projects.
Logistics for expansion joints present unique challenges. While smaller rubber joints are easily shipped, large metallic joints for power plants or bridge modules can be single-piece shipments requiring specialized heavy-lift transport and careful route planning. This logistical complexity adds cost and necessitates close coordination between manufacturer, engineering contractor, and end-user, often making local or regional supply strategically advantageous for large, critical projects.
The regulatory environment for trade is shaped by EU-wide directives and standards, such as the Pressure Equipment Directive (PED), which governs the design and manufacture of many expansion joints. Compliance with these standards is a non-negotiable market entry requirement and serves as a barrier against non-conforming imports. Furthermore, sustainability considerations are beginning to influence logistics, with a growing emphasis on optimizing transport to reduce the carbon footprint of the supply chain.
Price Dynamics
Pricing in the expansion joints market is far from commoditized and is determined by a complex set of factors. The cost structure is heavily influenced by raw material inputs, which can constitute a significant portion of the total product cost. Fluctuations in the prices of stainless steel, nickel alloys, specialty elastomers, and fluoropolymer linings directly and rapidly impact manufacturer input costs and, ultimately, market prices.
Beyond materials, the degree of engineering content and customization is a primary price driver. A standard, catalog rubber joint commands a very different price point than a custom-designed, multi-axial metallic joint for a nuclear power plant or a large bridge modular system. The value is embedded in the design expertise, rigorous testing, certification, and the assurance of long-term reliability in critical applications.
Competitive intensity varies by segment. The market for standardized products is highly price-sensitive, with competition from lower-cost global producers exerting downward pressure. In contrast, the market for highly engineered, application-specific solutions is less price-sensitive and more focused on technical performance, lifecycle cost, supplier reputation, and the quality of engineering support. In these segments, relationships and a proven track record are often as important as the initial purchase price.
Long-term contracts for large projects often include price adjustment clauses linked to raw material indices, transferring some commodity price risk from the manufacturer to the buyer. The overall price trend has been moderately upward, driven by persistent increases in energy, labor, and material costs. However, this trend is moderated by competitive pressures and the ability of large buyers to leverage their purchasing power for favorable terms.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment in the European expansion joints market is structured yet fragmented. A handful of global players compete across the full spectrum of products and end-markets, while numerous specialized firms dominate specific niches. The competitive strategies employed vary significantly based on company size and focus area.
The leading multinational corporations compete on the basis of their extensive product portfolios, global service and distribution networks, large-scale R&D investments, and their ability to serve as single-source suppliers for major engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) contractors. Their strength lies in providing integrated solutions and serving mega-projects worldwide.
Key competitive factors for all players include:
- Technical Expertise and Certification: Deep application knowledge and possession of necessary certifications (e.g., PED, nuclear codes) are fundamental barriers to entry.
- Product Quality and Reliability: Given the critical safety role of expansion joints, a flawless quality record is non-negotiable for securing business in core industries.
- Engineering and Service Support: The ability to provide pre-sales design assistance and post-sales technical support is a major differentiator, especially for complex installations.
- Lead Times and Flexibility: The capacity to react quickly to urgent maintenance needs or project changes provides a competitive edge.
Market consolidation has been a ongoing trend, with larger players acquiring smaller specialists to gain access to proprietary technologies, niche markets, or enhanced engineering capabilities. However, the market remains conducive to the existence of focused SMEs that cultivate deep relationships within a specific geographic region or industrial vertical, where their agility and specialized knowledge are valued over the scale of larger rivals.
Methodology and Data Notes
This report on the Europe Expansion Joints Market employs a rigorous, multi-faceted methodology designed to ensure analytical depth, accuracy, and actionable insight. The foundation of the analysis is a quantitative market model that synthesizes data from a wide array of primary and secondary sources to estimate market size, segmentation, and historical trends up to the base year of the 2026 edition.
Primary research forms a critical pillar of the methodology. This involves structured interviews and surveys conducted with industry stakeholders across the value chain. Participants include executives and product managers at expansion joint manufacturing companies, procurement specialists and engineers at leading end-user firms, technical experts from engineering consultancies, and representatives from industry associations. These interviews provide ground-level perspective on demand patterns, pricing, competitive dynamics, and technological trends that cannot be captured by purely statistical analysis.
Secondary research is conducted exhaustively to cross-verify and contextualize primary findings. This encompasses analysis of company annual reports, financial statements, and press releases; review of technical publications and industry journals; monitoring of project announcements and tender databases; and synthesis of relevant macroeconomic, trade, and industrial production data from official European and national statistical bodies. This triangulation of data sources mitigates bias and enhances the robustness of the conclusions.
The forecast component of the report, extending to 2035, is developed through a scenario-based approach. It integrates the historical quantitative model with qualitative insights on driver trajectories. Key macroeconomic indicators (GDP growth, industrial production indices, construction output), sector-specific investment forecasts (e.g., in energy transition, transportation), and regulatory timelines are analyzed to build a coherent projection of future demand. The report clearly distinguishes between observed historical data and forward-looking projections, acknowledging the inherent uncertainties in long-range forecasting.
Outlook and Implications
The European expansion joints market from 2026 to 2035 is projected to follow a path of steady, incremental growth, punctuated by regional and sectoral variations. The overarching narrative is one of a market supported by enduring fundamentals—infrastructure aging, regulatory mandates, and the imperative of operational safety—while being gradually reshaped by the continent’s strategic priorities, notably the green transition and digital modernization.
The energy transition will be a dominant force shaping demand. The phasedown of traditional fossil-fuel assets will impact related maintenance markets, but this will be counterbalanced, and likely exceeded, by investments in renewable energy infrastructure, hydrogen production and distribution networks, carbon capture utilization and storage (CCUS) systems, and modernized electrical grids. Each of these emerging areas presents specific, often technically demanding, requirements for expansion joint systems, favoring suppliers with strong innovation capabilities.
Technological evolution within the product itself will accelerate. The integration of smart monitoring technologies, such as embedded sensors to track movement, stress, temperature, and leakage in real-time, will transition expansion joints from passive components to active elements of predictive maintenance systems. This “smart joint” trend will create value-added opportunities for manufacturers and change the basis of competition towards digital service offerings and data analytics.
For industry participants, the implications are clear. Manufacturers must invest in R&D to develop solutions for new applications in the hydrogen and CCUS value chains. They must also enhance operational efficiency to manage cost pressures and consider strategic partnerships to access new technologies or markets. For end-users and investors, understanding the shifting geographic and sectoral demand hotspots will be crucial for capital allocation. The market promises resilience but rewards foresight, technical agility, and a deep understanding of the evolving infrastructure landscape that defines the European economy through 2035 and beyond.
Source: IndexBox Platform