Executive Summary
The Egyptian expansion joints market is positioned at a critical juncture, shaped by a confluence of national infrastructure ambitions, industrial modernization efforts, and the pressing need to upgrade aging facilities. As of the 2026 analysis, the market demonstrates robust fundamentals driven by sustained investment in construction, energy, and utilities. Expansion joints, essential components for accommodating thermal movement, seismic activity, and structural settlement in pipelines, bridges, and buildings, are seeing their demand profile evolve in line with Egypt’s economic development trajectory.
This report provides a comprehensive examination of the market’s current state, dissecting the complex interplay between supply-side capabilities, import dependencies, and end-user sector demand. The analysis extends through a forecast horizon to 2035, outlining the structural trends, competitive shifts, and potential disruptions that will define the market’s future. Understanding these dynamics is paramount for stakeholders across the value chain, from global manufacturers and local fabricators to engineering firms and project owners.
The core narrative of the market is one of growth constrained by logistical and production challenges. While domestic manufacturing exists, particularly for standard applications, a significant portion of demand for specialized, high-performance joints is met through imports. The market’s progression towards 2035 will be heavily influenced by government policy, foreign currency availability for imports, and the success of local industry in moving up the value chain to capture more complex, high-margin product segments.
Market Overview
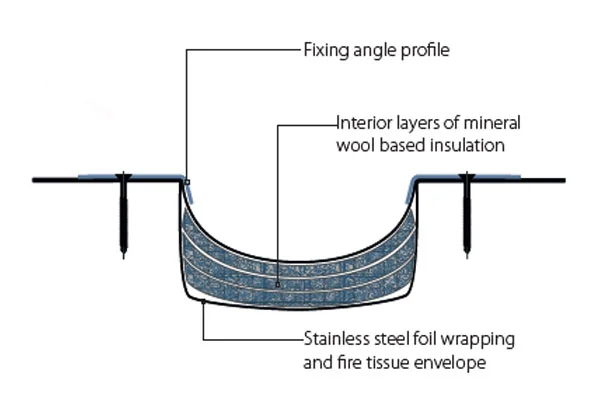
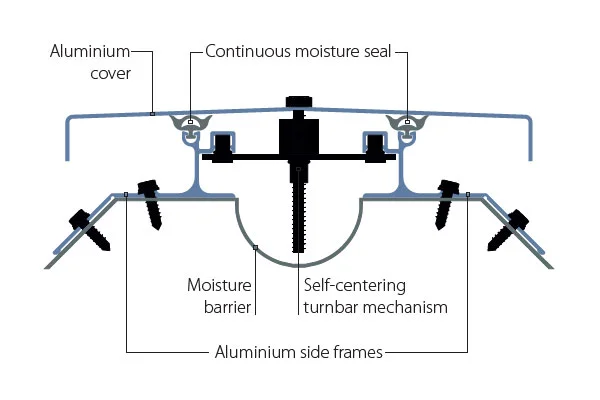
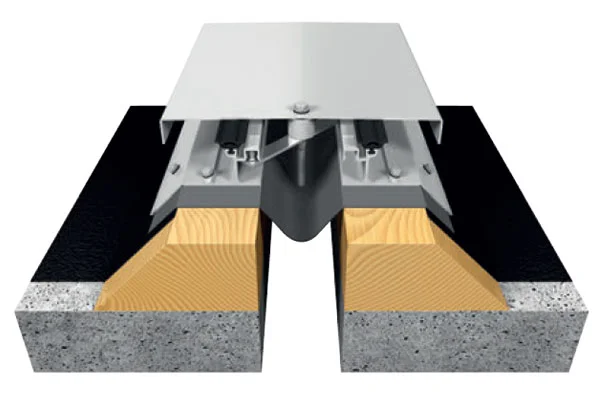
The Egyptian market for expansion joints is a specialized segment within the broader industrial and construction supplies sector. Its size and characteristics are directly tied to the volume and type of large-scale projects underway across the country. The market encompasses a wide range of product types, including metallic bellows joints, rubber joints, fabric joints, and specialized joints for high-pressure or corrosive environments. Each category serves distinct applications, with demand varying significantly by end-use industry.
Geographically, market activity is concentrated around major economic and industrial hubs. The Greater Cairo region, Alexandria, and the Suez Canal Economic Zone (SCZone) represent primary demand centers due to the density of industrial plants, power generation facilities, and urban infrastructure projects. New administrative capitals and planned cities also generate substantial demand, often for modern, integrated building systems that incorporate advanced expansion joint solutions.
The market structure is bifurcated, featuring both the supply of finished goods and the provision of design, engineering, and installation services. While some projects procure joints directly, many are specified and supplied as part of larger mechanical or structural packages by engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) contractors. This integrated procurement model places significant influence in the hands of specifying engineers and project managers, who determine technical requirements and often influence brand selection.
Regulatory and standards compliance forms a critical layer of the market environment. Products must adhere to Egyptian standards, which often align with international norms such as ISO, ASTM, or EJMA (Expansion Joint Manufacturers Association) standards. Certification and approval processes can impact time-to-market for new suppliers and are a key consideration for project owners, particularly in state-led infrastructure and energy projects where technical compliance is rigorously enforced.
Demand Drivers and End-Use
Demand for expansion joints in Egypt is fundamentally derived from investment in fixed assets. The market is not cyclical in a traditional consumer sense but follows the investment cycles of key capital-intensive industries. The primary demand drivers are multi-year national projects and the ongoing need for industrial maintenance and expansion. As such, understanding the pipeline of public and private sector investments provides the clearest indicator of future market direction.
The construction and infrastructure sector stands as the largest end-user. This includes:
- Transport Infrastructure: Bridges, highways, airport terminals, and railway networks require expansion joints to handle thermal expansion and dynamic loads. Projects like the monorail systems, new high-speed rail, and continuous road expansions are persistent demand sources.
- Commercial & Public Buildings: Large-scale structures such as the New Administrative Capital’s government complexes, commercial towers, hospitals, and stadiums incorporate joints in parking decks, floor slabs, and facades.
- Water & Wastewater Treatment: Massive national projects to improve water security and sanitation drive demand for joints in large-diameter pipelines, treatment plant structures, and outfall systems.
The energy sector is the second major pillar of demand, characterized by high technical specifications.
- Oil & Gas: Upstream, midstream, and downstream facilities all utilize expansion joints. Applications range from offshore platform piping and refinery process lines to LNG terminal transfer systems. The push to develop Mediterranean gas fields and modernize refineries sustains this segment.
- Power Generation: Thermal power plants (both conventional and combined-cycle) require joints for turbine connections, boiler feed lines, and flue gas ducts. Furthermore, investments in renewable energy, particularly large-scale solar installations, create demand for specialized joints in solar thermal systems and supporting infrastructure.
Industrial manufacturing forms a steady, if less volatile, demand base. Cement plants, steel mills, chemical processing facilities, and fertilizer complexes all rely on expansion joints for their piping networks and equipment connections. Demand here is driven by greenfield projects, plant capacity expansions, and the essential cycle of maintenance, repair, and operations (MRO) activities. The government’s focus on import substitution and industrial localization could spur new manufacturing projects, further bolstering this segment.
Supply and Production
The supply landscape for expansion joints in Egypt is characterized by a mix of domestic manufacturing and significant import reliance. Local production is primarily focused on standard, low-to-medium pressure metallic bellows joints and basic rubber joints. These are often fabricated by mid-sized industrial workshops and specialized metal fabrication companies that serve regional construction and MRO markets. Their competitive advantage lies in shorter lead times, lower costs for standard items, and adaptability to local project requirements.
However, for high-specification applications—such as those in the oil & gas, power generation, and major infrastructure sectors—the market depends heavily on imports. These critical joints require advanced engineering, specialized materials (e.g., high-grade stainless steels, Inconel, PTFE), and rigorous quality control that is often beyond the current technical or economic scope of most local producers. Consequently, international manufacturers from Europe, Asia, and the Americas hold a dominant position in these high-value segments, typically supplying through local agents or distributors.
The domestic production capability is evolving. A few established Egyptian engineering companies have developed competencies in manufacturing more technically demanding joints, often through technology transfer agreements or joint ventures with foreign partners. Their growth is supported by government tenders that include local content requirements, providing a protected niche. The key constraints for local industry expansion include access to advanced manufacturing technology, the high cost of quality raw materials (often imported), and a shortage of highly specialized welding and design engineers.
The supply chain for raw materials is a critical factor. The availability and pricing of key inputs like stainless-steel sheets, bellows-quality alloys, and specialized elastomers directly impact production costs and lead times. Since many of these materials are imported, domestic manufacturers are exposed to global commodity price fluctuations and foreign exchange volatility. This vulnerability underscores the interconnected nature of the market, where local supply stability is often contingent on global trade dynamics.
Trade and Logistics
International trade is a defining feature of the Egyptian expansion joints market. Given the gap between domestic production capabilities and project specifications, imports fulfill a substantial portion of total market demand. The import flow is diverse, sourcing products from established manufacturing hubs worldwide. European suppliers (from Germany, Italy, and France) are traditionally associated with high engineering quality and are preferred for complex infrastructure and energy projects. Asian manufacturers, particularly from China, India, and South Korea, compete aggressively on price for standard and medium-specification joints, gaining significant market share in cost-sensitive segments.
The logistics of importing these often-bulky and sometimes delicate components present challenges. Expansion joints, especially large-diameter metallic units, require careful handling and transportation. Import channels typically involve sea freight to major ports like Port Said, Alexandria, or Sokhna. Efficient customs clearance is crucial to avoid project delays, making the role of experienced local import agents and customs brokers vital. These intermediaries not only manage logistics but also navigate the regulatory landscape, ensuring compliance with standards and certification requirements.
Egypt also functions as a potential re-export hub for the wider North and East Africa region, though this role is currently secondary to serving the domestic market. The strategic location of the Suez Canal and developed port infrastructure provides a logistical advantage. Some international suppliers establish regional warehouses or assembly facilities in Egypt to serve both the local market and neighboring countries, reducing lead times and offering better technical support.
Trade policy and currency management are paramount concerns. Changes in import tariffs, value-added tax (VAT) on industrial goods, or the imposition of anti-dumping duties can immediately alter the cost structure for end-users. More significantly, the availability of foreign currency for import letters of credit can act as a severe constraint, delaying or even canceling procurements. Periods of currency devaluation sharply increase the cost of imported joints, prompting project owners to reconsider specifications, seek local alternatives where possible, or delay projects, thereby introducing volatility into market demand.
Price Dynamics
Pricing in the Egyptian expansion joints market is not uniform but is stratified by product type, specification, and origin. A multi-tiered price structure exists, reflecting the vast difference between a standard rubber joint for a building and a customized, high-alloy metallic joint for a refinery. For standardized products, competition is intense, and prices are largely determined by global commodity costs (especially metals) and the competitive pressure from Asian imports. In this segment, Egyptian manufacturers compete directly on price, often with slim margins.
For engineered, made-to-order joints, pricing is project-specific and follows a cost-plus model. The final price incorporates raw material costs (highly sensitive to global nickel and specialty alloy prices), engineering design hours, manufacturing complexity, testing and certification costs, profit margin, and logistics. In this high-end segment, European and American brands command a significant price premium based on perceived reliability, technical support, and a proven track record in critical applications. This premium is often justified in tender evaluations through lifecycle cost analyses that emphasize durability and reduced maintenance.
Currency exchange rate volatility is arguably the single most influential macro-factor on market pricing. Given the import dependency for materials and finished goods, a depreciation of the Egyptian pound against the US dollar and Euro directly and rapidly increases the landed cost of imports. This inflationary pressure is often passed through the supply chain, leading to budget overruns for projects priced in local currency. It can also trigger a shift in procurement strategies, with clients sometimes opting for lower-specification alternatives or pushing for extended payment terms to manage cash flow.
Payment terms themselves are a critical component of the commercial landscape. Public sector projects often involve protracted payment cycles, which can strain the working capital of suppliers and distributors. In contrast, private sector and foreign-funded projects may offer more reliable payment schedules. The negotiation of payment terms—including advance payments, letters of credit, and retention amounts—is a key commercial skill for suppliers and significantly affects the net realized price and risk profile of any sale.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment is fragmented and segmented by product category and target market. No single player holds a dominant share across all segments. Instead, the landscape is populated by distinct groups of competitors, each with its own strategic focus and value proposition. The interplay between these groups defines market rivalry and shapes the options available to buyers.
At the top tier are the global engineering-focused manufacturers. These are typically multinational corporations with a strong brand reputation, extensive R&D capabilities, and a global presence. They compete almost exclusively in the high-specification segment for mega-projects in energy and major infrastructure. Their strategy revolves around technical superiority, direct engagement with EPC contractors and project owners, and providing comprehensive engineering support. They often operate through dedicated local offices or exclusive partnerships with well-established Egyptian engineering firms.
The middle tier consists of regional international players and the more advanced local manufacturers. This group includes:
- Asian manufacturers competing on a value-for-money proposition.
- Egyptian companies that have invested in technology to produce intermediate-specification joints.
- Local agents representing a portfolio of international brands across different price points.
This tier is characterized by fierce competition, with players vying for projects in commercial construction, water treatment, and industrial plant MRO. Success here often depends on a combination of competitive pricing, reliable delivery, and responsive customer service.
The lower tier comprises numerous small local fabricators and workshops. They produce very basic expansion joints and related piping components, primarily for the local construction aftermarket and small-scale industrial applications. Competition in this segment is almost purely price-based, with minimal differentiation. However, these firms are highly agile and serve an important role in meeting the demand for quick, low-cost solutions.
Key competitive factors extend beyond price. Technical advisory capability, the ability to provide certified design calculations and stress analysis, after-sales service and technical support, and a proven project track record are all critical determinants in winning business, especially for complex applications. Furthermore, navigating the bureaucratic tender processes for public sector projects requires deep local knowledge and relationships, which can be a significant barrier to entry for new foreign suppliers without a strong local partner.
Methodology and Data Notes
This report is built upon a multi-faceted research methodology designed to triangulate data and provide a holistic, accurate view of the Egyptian expansion joints market. The core approach integrates quantitative data gathering with qualitative expert analysis to ensure both statistical robustness and contextual depth. The findings presented are the result of a systematic process aimed at minimizing bias and maximizing reliability.
Primary research formed the backbone of the analysis. This involved a extensive program of structured interviews and surveys with key industry participants across the value chain. Participants included:
- Senior executives and sales managers at local manufacturing facilities.
- Importers, distributors, and agents of international brands.
- Procurement managers and specifying engineers at leading EPC contractors.
- Project owners and facility managers in key end-user industries (oil & gas, power, construction).
- Industry experts, consultants, and trade association representatives.
These engagements provided firsthand insights into market dynamics, pricing trends, competitive behavior, and operational challenges.
Secondary research was conducted to validate and supplement primary findings. This encompassed a thorough review of:
- Official government statistics on construction activity, industrial production, and international trade (HS codes relevant to expansion joints).
- Financial reports and public announcements from publicly traded companies in related sectors.
- Tender databases and project tracking services to gauge the pipeline of demand.
- Technical publications, industry journals, and relevant engineering standards.
Data from disparate sources was cross-referenced to build a consistent and coherent market picture.
The forecasting approach to 2035 is scenario-based and qualitative, focusing on directional trends rather than invented absolute figures. It considers the interplay of identified macroeconomic variables, policy directions, and industry-specific drivers. The analysis models potential outcomes based on different assumptions regarding economic growth, infrastructure investment cycles, import policy, and the pace of local industry development. This report explicitly does not generate new absolute market size or forecast numbers but provides the analytical framework to understand the range of possible market evolutions over the coming decade.
Outlook and Implications
The trajectory of the Egyptian expansion joints market towards 2035 will be inextricably linked to the nation’s broader economic and industrial fortunes. The underlying demand fundamentals remain strong, anchored by long-term infrastructure plans, population growth, and energy sector development. However, the path will not be linear; it will be shaped by a series of critical factors that will determine the market’s size, structure, and profitability for various players. Stakeholders must navigate this landscape with a clear understanding of both opportunities and persistent challenges.
On the demand side, the market is expected to see a gradual sophistication of requirements. As Egypt undertakes more complex projects—such as green hydrogen facilities, advanced desalination plants, and next-generation industrial zones—the specifications for expansion joints will become more demanding. This trend favors technically adept suppliers who can provide integrated engineering solutions rather than just products. Concurrently, the MRO market for existing infrastructure and industrial plants will provide a steady, recurring revenue stream, particularly as assets age and require refurbishment or replacement of components.
The supply-side evolution presents the most significant variable. The push for import substitution and industrial localization is a double-edged sword. It presents a monumental opportunity for capable Egyptian manufacturers to capture a larger share of the medium-specification market and to develop competencies in higher-value segments through partnerships or technology acquisition. Success in this arena would reduce foreign exchange outflow and create skilled jobs. However, this transition is capital- and knowledge-intensive. Its pace will depend on consistent policy support, access to financing, and the ability of local firms to achieve and maintain international quality standards to gain the trust of project specifiers.
For international suppliers, the market will continue to offer significant opportunities, but the competitive strategy must evolve. The era of simply exporting finished goods may gradually give way to more localized engagement models. These could include establishing local assembly or final testing facilities, forming deeper technical partnerships with Egyptian firms, or investing in local inventory to improve service levels. Navigating currency risk and developing flexible commercial terms will remain essential skills. The winners will be those who combine global technical expertise with a truly localized, agile, and partnership-oriented approach to the Egyptian market.
In conclusion, the Egyptian expansion joints market from 2026 to 2035 is poised for growth but will be characterized by increasing complexity and competition. The interplay between government policy, global economic conditions, and local industrial capability will define the new equilibrium. For all participants—buyers, suppliers, and investors—success will require moving beyond transactional thinking. It will demand strategic foresight, technical excellence, and a nuanced understanding of the unique operational and commercial realities of the Egyptian industrial landscape. This report provides the foundational analysis upon which such strategic decisions can be confidently made.
Source: IndexBox Platform