Executive Summary
The global market for building seismic joints represents a critical and specialized segment within the broader construction and infrastructure safety industry. These engineered components are designed to absorb and accommodate the dynamic movements caused by seismic events, thermal expansion, and wind sway, thereby preserving structural integrity and preventing catastrophic failure. The market’s evolution is intrinsically linked to the convergence of stringent building safety regulations, increasing urbanization in seismically active zones, and a growing emphasis on the resilience of critical infrastructure. This report provides a comprehensive 2026 baseline analysis and a strategic forecast to 2035, examining the interplay of these fundamental forces.
Current market dynamics are characterized by a complex supply chain involving high-performance material manufacturers, specialized engineering firms, and construction contractors. Demand is bifurcated between new construction projects, particularly high-rise buildings and long-span structures, and the retrofitting of existing buildings to meet modern seismic codes. The competitive landscape features a mix of large multinational corporations with broad product portfolios and smaller, niche players offering customized solutions for specific structural challenges. This report dissects these segments to provide a granular view of the market structure.
The outlook to 2035 is shaped by several megatrends, including the adoption of performance-based seismic design, the integration of smart monitoring sensors within joint systems, and the escalating economic costs of natural disasters. While advanced economies with mature building codes will continue to drive product innovation, the most significant volume growth is anticipated in emerging economies within the Asia-Pacific and Latin American seismic belts. This analysis equips stakeholders with the data and insights necessary to navigate regulatory shifts, assess competitive threats, and identify long-term growth vectors in a market where safety and performance are paramount.
Market Overview
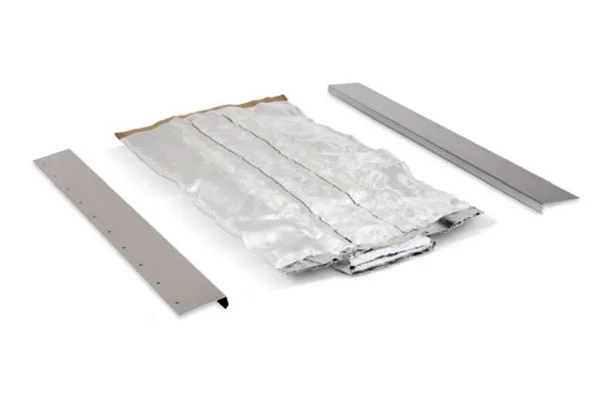
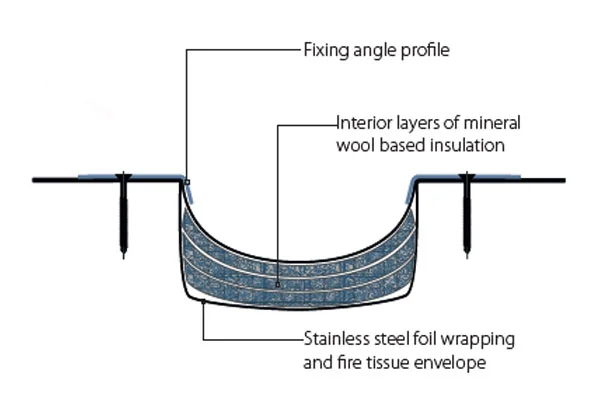
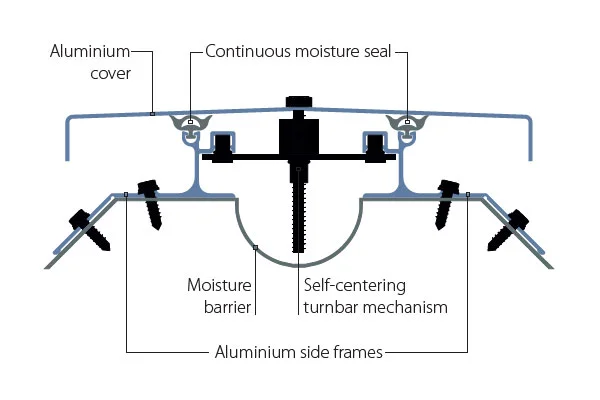
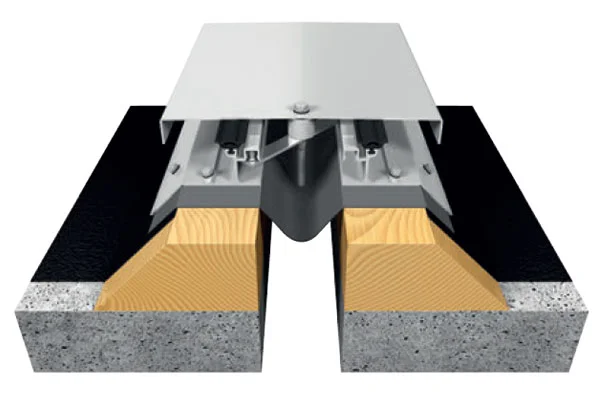
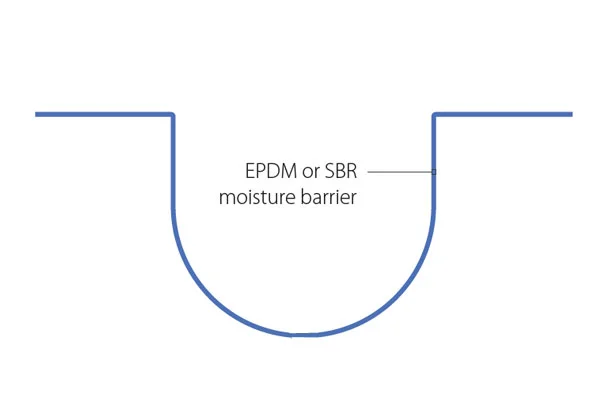
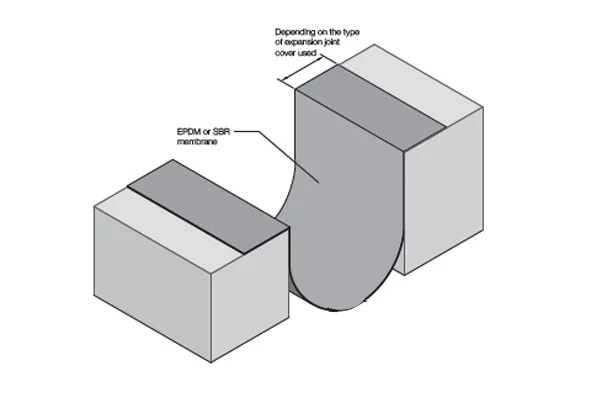
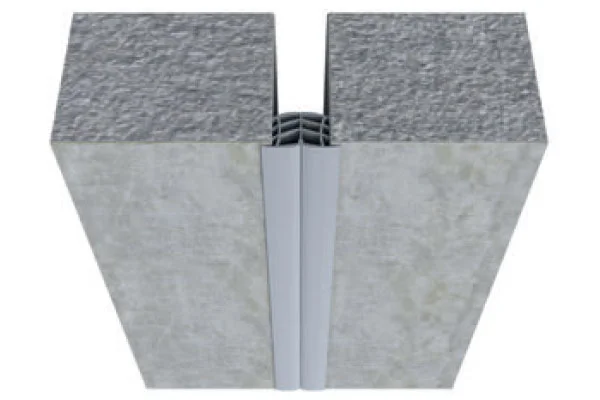
The world building seismic joints market is a technology-driven sector focused on mitigating the impact of earth movements on constructed facilities. These joints are not mere gaps but sophisticated assemblies comprising seals, movement accommodation devices, and load-transfer elements. The market encompasses a wide array of product types, including expansion joints, control joints, and isolation bearings, each engineered for specific movement capacities and structural roles. The sector’s value is derived from both the manufactured components and the associated design, testing, and installation engineering services.
Geographically, the market is heavily influenced by tectonic activity and the corresponding regulatory environment. Regions such as the Pacific Ring of Fire, encompassing Japan, New Zealand, the western coasts of North and South America, and Southeast Asia, constitute the core demand centers. However, market growth is increasingly global, as seismic awareness rises in regions previously considered low-risk and as building codes for wind and thermal movement become more rigorous worldwide. The market’s development stage varies significantly, from saturated and innovation-focused in Japan to nascent and regulation-driven in parts of Africa and the Middle East.
The market structure is segmented by product type, material (elastomeric, metallic, laminated), application (residential, commercial, industrial, infrastructure), and end-use (new construction vs. retrofit). The infrastructure segment, including bridges, airports, and hospitals, commands a premium due to the critical nature of these assets and the severe consequences of their failure. This report provides a detailed segmentation analysis, quantifying the size and growth trajectory of each key segment from the 2026 baseline and projecting their evolution through the forecast period to 2035.
Demand Drivers and End-Use
Primary demand for building seismic joints is propelled by the codification and enforcement of seismic safety standards. Following high-profile seismic disasters, governments and international bodies frequently revise and strengthen building codes, creating immediate compliance-driven demand. The global trend towards performance-based design codes, which mandate specific building behaviors during an earthquake rather than just prescribing minimum materials, is a significant catalyst. This shift necessitates more advanced and precisely engineered joint systems, moving the market up the value chain.
Urbanization patterns, particularly the proliferation of high-rise buildings and complex mega-structures in major cities, form a powerful underlying driver. As buildings become taller and architectural designs more ambitious, the induced movements from wind and thermal effects become as critical as seismic movements. Furthermore, the growing economic value concentrated in single buildings and infrastructure assets elevates the cost-benefit analysis, making investments in advanced seismic protection systems more justifiable. The protection of data centers, manufacturing clean rooms, and other vibration-sensitive operations also creates specialized demand.
The retrofit and renovation sector represents a substantial and growing end-use segment. A vast global inventory of older buildings, including historically significant structures, was constructed before modern seismic codes. Upgrading this existing building stock is a massive, long-term driver. Key end-user industries include commercial real estate development, public infrastructure projects, industrial plant construction, and the healthcare sector, where hospitals must remain operational post-disaster. This section analyzes the demand intensity and procurement patterns within each of these critical end-use sectors.
Supply and Production
The supply chain for building seismic joints is specialized and knowledge-intensive. Upstream, it relies on producers of high-grade materials such as specialized elastomers (e.g., neoprene, natural rubber), lead-core rubber, stainless steel, and PTFE (Teflon) for sliding surfaces. The manufacturing process involves precision molding, vulcanization, metal fabrication, and rigorous quality control testing. Production is characterized by relatively high barriers to entry due to the need for specialized engineering expertise, certification of products through extensive physical testing (e.g., on shake tables), and established trust with structural engineering firms.
Geographically, production is concentrated in regions with both advanced manufacturing capabilities and a history of seismic research. This includes established hubs in Japan, the United States, Italy, and New Zealand. However, localization of production is increasing, with manufacturing footprints expanding in China, India, and Turkey to serve regional markets and leverage cost advantages. The production landscape is adapting to trends such as the demand for longer-lasting, low-maintenance joints and systems that can be installed more quickly to reduce on-site construction time.
Capacity utilization and technological innovation are key themes. Leading suppliers invest heavily in R&D to develop next-generation products with higher damping coefficients, integrated health monitoring sensors, and improved fire resistance. The supply side is also responding to sustainability trends, with research into more recyclable materials and longer-lifecycle products. This report details the global production capacity distribution, key manufacturing processes, and the innovation roadmap that is shaping the future of supply.
Trade and Logistics
International trade in building seismic joints is a function of project specificity and regional technical expertise. While bulk, standardized components may be sourced globally, highly engineered or custom-designed systems for landmark projects often involve direct contracts with specialized manufacturers regardless of location. Major export flows originate from countries with leading seismic engineering industries, serving global engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) firms working on international projects. Trade patterns are thus closely tied to the global footprint of major construction and engineering conglomerates.
Logistics present unique challenges due to the nature of the products. Many seismic isolation bearings and large joint assemblies are heavy, high-volume items requiring specialized handling and transportation. For time-sensitive retrofit projects, especially in post-disaster recovery scenarios, air freight may be utilized for critical components. Furthermore, the need for just-in-sequence delivery to congested construction sites in urban centers demands sophisticated supply chain coordination. Tariffs and non-tariff barriers, such as country-specific certification requirements, can also influence trade routes and local partnership strategies.
The trend towards regionalization of supply chains, accelerated by global trade uncertainties and a focus on resilience, is encouraging more local manufacturing and assembly. However, the export of engineering design services and proprietary technology remains a significant aspect of trade. This analysis examines major trade corridors, the impact of regional trade agreements, and the logistical considerations that affect landed cost and project scheduling for international suppliers.
Price Dynamics
Pricing in the building seismic joints market is far from commoditized; it is determined by a complex matrix of value-based and cost-based factors. The primary determinant is the engineering performance specification: movement capacity, load rating, damping characteristics, and fire-resistance rating. A custom-designed lead-rubber bearing for a hospital will command a significantly higher price per unit than a standard expansion joint profile for a parking garage. Therefore, price analysis must be conducted at the segment and application level to be meaningful.
Cost pressures stem from raw material inputs, particularly specialty elastomers and metals, whose prices fluctuate with global commodity markets. Labor costs for skilled fabrication and stringent quality control also constitute a major portion of the cost structure. However, competitive pressure often centers on total installed cost and lifecycle value rather than just component price. A more expensive, but more durable and lower-maintenance system, can be more economical over the lifespan of a building, a value proposition that leading suppliers emphasize.
Regional price disparities exist due to variations in local material costs, labor rates, regulatory testing requirements, and the competitive density of suppliers. In markets with few certified local suppliers, prices may be higher. The report analyzes historical price trends across key product categories and regions, identifying the key levers of cost and value. It also explores the pricing strategies employed in different sales channels, from direct bidding on major infrastructure projects to distribution through construction material suppliers.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive arena is moderately consolidated, featuring a blend of global specialists and regional champions. A handful of multinational corporations dominate the high-end market for seismic isolation and damping systems, leveraging extensive R&D portfolios, global certification credentials, and long-standing relationships with top-tier engineering firms. Their competition is based on technological leadership, proven performance in real earthquakes, and the ability to provide full-system design support.
At the same time, numerous medium-sized and smaller companies compete effectively in specific niches or geographic regions. These players may focus on specific product types (e.g., architectural expansion joint covers), particular materials, or the retrofit market for smaller buildings. Competition in these segments often revolves around cost-effectiveness, flexibility, speed of delivery, and strong local sales and service networks. The landscape is also characterized by strategic partnerships, where material suppliers, joint manufacturers, and engineering firms collaborate to offer integrated solutions for major projects.
- Key competitive factors include: proprietary material formulations and product designs; a portfolio of successfully tested and certified systems; a global or strong regional project reference list; depth of in-house engineering expertise; and the ability to offer digital tools for joint selection and specification.
- Market share is contested through: direct engagement with structural engineers and specifiers; participation in international code-writing committees; strategic acquisitions to fill product or geographic gaps; and investment in digital marketing and detailed technical literature.
This report provides a detailed mapping of the competitive landscape, profiling the strategies, strengths, and weaknesses of leading players, and analyzing the merger and acquisition activity that is reshaping the industry.
Methodology and Data Notes
This report on the World Building Seismic Joints Market has been developed using a rigorous, multi-layered methodology designed to ensure accuracy, relevance, and strategic depth. The core approach integrates quantitative market sizing with qualitative industry analysis. Primary research forms the foundation, involving in-depth interviews with key industry stakeholders across the value chain. This includes executives from leading seismic joint manufacturers, raw material suppliers, prominent structural engineering consultants, contractors specializing in seismic retrofit, and procurement officials from large development firms.
Secondary research complements and validates primary findings, encompassing a thorough review of technical publications, international building codes (IBC, Eurocode, etc.), company annual reports and financial statements, global trade databases, and project tender announcements for major infrastructure works. Market size estimates and segmentations are built using a bottom-up approach, aggregating data from demand analysis in key countries and applications, cross-verified with a top-down review of the construction industry’s investment in seismic safety measures.
The forecast model to 2035 is based on the identification and quantification of key macroeconomic, regulatory, and industry-specific drivers. It employs a combination of time-series analysis, regression modeling against leading indicators (e.g., construction output in seismic zones, frequency of code updates), and scenario analysis to account for potential disruptions. All data is subjected to a multi-step validation process to ensure internal consistency and alignment with observable industry trends. This transparent methodology ensures the report provides a reliable and actionable foundation for strategic decision-making.
Outlook and Implications
The trajectory of the world building seismic joints market to 2035 is poised for sustained growth, underpinned by non-negotiable trends in safety, urbanization, and climate resilience. The transition from prescriptive to performance-based seismic design codes will accelerate globally, fundamentally shifting demand towards higher-value, engineered-to-order systems and integrated damping solutions. This evolution will reward companies with strong R&D capabilities and deep engineering integration skills, potentially raising barriers to entry in the most technologically advanced segments of the market.
Geographically, while established markets will remain vital centers of innovation and premium demand, the growth epicenter will shift markedly towards emerging economies in seismically active regions of Asia, Latin America, and the Middle East. This shift presents both opportunity and challenge: opportunity in terms of market volume, but challenge in navigating diverse regulatory environments, price sensitivity, and the need for localized supply chains and partnerships. The retrofit market, driven by mandatory upgrade programs for public buildings and schools, will emerge as a massive, long-wave opportunity, particularly in earthquake-prone developed countries with aging infrastructure.
Strategic implications for industry stakeholders are profound. For manufacturers, success will hinge on portfolio diversification, investment in smart and sustainable product technologies, and strategic positioning in high-growth regions. For engineering and construction firms, mastering the specification and integration of advanced seismic systems will become a key differentiator. For investors and new entrants, the market offers attractive niches in specialized materials, digital design tools, and retrofit solutions. Ultimately, the market’s future will be defined by its contribution to building a more resilient global infrastructure, making it not only an economic arena but a critical component of societal safety and sustainability.
Source: IndexBox Platform