Executive Summary
The Vietnamese market for polyurethane sealants stands as a dynamic and critical segment within the nation’s broader construction and industrial materials sector. Characterized by robust growth driven by sustained infrastructure investment, urbanization, and a burgeoning manufacturing base, the market presents significant opportunities alongside evolving competitive and logistical challenges. This report provides a comprehensive 2026 analysis of the market’s structure, key players, demand determinants, and supply dynamics, extending its perspective through a strategic forecast to 2035.
Current market expansion is fundamentally linked to the performance of key end-use industries, most notably construction, automotive assembly, and furniture production. Government-led infrastructure projects and private real estate development create persistent demand for high-performance sealing solutions in both residential and commercial applications. Simultaneously, the growth of domestic manufacturing and export-oriented industries necessitates reliable sealants for product assembly and durability, further stimulating market volume.
The supply landscape is a mix of international chemical conglomerates and increasingly capable domestic producers. Competition is intensifying on fronts of product innovation, pricing, and distribution network reach. Furthermore, Vietnam’s trade profile shows a consistent reliance on imports for specific high-grade formulations and raw materials, while also developing its export capacity for standard products within the ASEAN region. Understanding these trade flows and the underlying price sensitivity to raw material costs is essential for strategic positioning.
Looking ahead to 2035, the market is anticipated to navigate a path defined by technological advancements, sustainability imperatives, and evolving regulatory standards. The long-term outlook will be shaped by the pace of industrial upgrading, the adoption of green building standards, and Vietnam’s integration into global supply chains. This report delivers the granular data and strategic analysis necessary for stakeholders to benchmark performance, identify growth avenues, and formulate resilient, long-term strategies in this evolving landscape.
Market Overview
The polyurethane sealants market in Vietnam is a mature yet growing segment of the specialty chemicals industry, integral to a wide array of sealing, bonding, and waterproofing applications. As of the 2026 analysis period, the market has consolidated its position following years of expansion, now entering a phase of qualitative growth and product segmentation. The market’s value and volume are directly correlated with the cyclical trends in construction and the secular growth trends in manufacturing, making its trajectory a reliable indicator of broader industrial health.
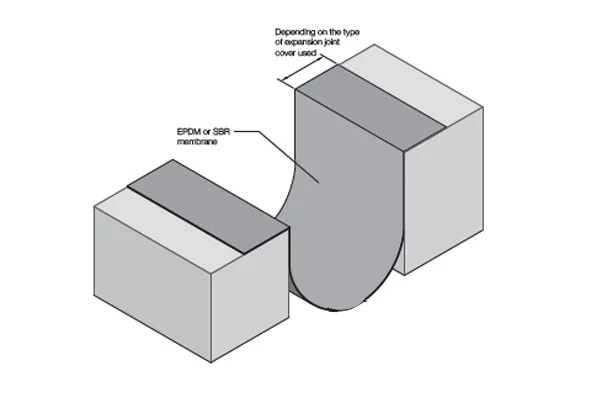
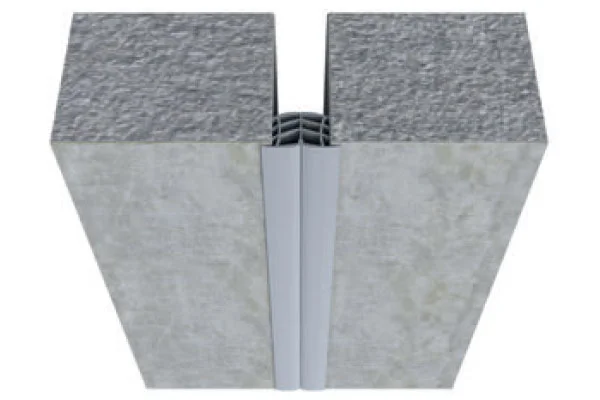
Market segmentation typically follows both product formulation and end-use application. Product-wise, distinctions are made between one-component and two-component systems, as well as between standard, low-modulus, and high-performance (e.g., aerospace-grade) variants. Application segments are clearly delineated, with construction (including glazing, flooring, and expansion joints) representing the dominant share, followed by industrial assembly in automotive, shipbuilding, and furniture, and finally, the DIY and maintenance sector which is smaller but growing in urban centers.
The regulatory environment in Vietnam is becoming increasingly structured, influencing market standards. National technical regulations on construction materials and growing awareness of volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions are prompting manufacturers to reformulate products. While compliance levels vary, this regulatory push is gradually shifting the market toward higher-quality, more environmentally considerate products, creating a competitive edge for producers with strong R&D capabilities.
Geographically, demand is heavily concentrated in key economic regions. The Ho Chi Minh City metropolitan area and the Southeast region, along with the Hanoi and Red River Delta region, account for the majority of consumption due to their density of construction projects and industrial parks. However, secondary cities and industrial corridors, such as those in the Central Coast (Da Nang) and the Mekong Delta, are emerging as new growth frontiers, driven by regional development policies and infrastructure decentralization.
Demand Drivers and End-Use
Demand for polyurethane sealants in Vietnam is propelled by a confluence of macroeconomic, industrial, and social factors. The primary and most potent driver remains the relentless pace of urbanization and concomitant infrastructure development. National and municipal governments continue to prioritize large-scale transport projects—including expressways, metro lines, and airport expansions—which require substantial volumes of durable, weather-resistant sealants for joints, panels, and structural elements.
The construction sector’s appetite is bifurcated between public infrastructure and private real estate. The residential real estate market, despite periodic corrections, demonstrates long-term demand fundamentals due to population growth and urban migration, fueling need for sealants in both high-rise apartments and individual housing. Concurrently, the development of office complexes, retail spaces, hotels, and industrial warehouses underlines robust commercial and industrial construction activity, each with specific sealing requirements for facades, roofs, and interiors.
Beyond construction, the manufacturing sector is a critical and sophisticated consumer. The automotive industry, with its expanding assembly and parts production base, utilizes polyurethane sealants for windshield bonding, panel assembly, and vibration damping. The electronics and appliance manufacturing sector requires precision sealants for encapsulation and protection. Furthermore, the furniture industry, a major export earner for Vietnam, relies on these products for assembly and finishing, with demand closely tied to global export orders.
Emerging demand drivers include the gradual adoption of green building standards (such as LOTUS or LEED) and increasing maintenance, repair, and operations (MRO) activities. Green certifications often specify low-VOC and high-durability materials, favoring advanced polyurethane formulations. The MRO segment, while smaller, is growing as Vietnam’s building stock ages and as industrial facilities require ongoing maintenance, creating a steady, recurring demand stream that is less cyclical than new construction.
Supply and Production
The supply side of Vietnam’s polyurethane sealants market is characterized by a tiered competitive structure involving multinational corporations, regional players, and domestic manufacturers. Leading global chemical companies maintain a significant presence, often through local subsidiaries or joint ventures, leveraging their advanced technology, brand reputation, and extensive product portfolios. These players typically dominate the high-end segment, catering to specification-driven projects in construction and demanding industrial applications.
Domestic production capacity has seen considerable investment and enhancement over the past decade. Local manufacturers have progressed from producing basic, generic formulations to developing more specialized products that compete in the mid-range market. Their competitive advantages often lie in lower production costs, agility in serving local distributors, and a deep understanding of regional customer preferences and price sensitivity. Several have achieved requisite quality certifications to supply to larger contractors and export markets.
Production infrastructure is primarily located near consumption hubs and key logistics nodes. Major manufacturing facilities are clustered in industrial zones in the provinces surrounding Ho Chi Minh City and Hanoi, as well as in key port cities. This strategic placement minimizes logistics costs for both sourcing raw materials—many of which are imported—and distributing finished goods to dense market areas. The scale of operations ranges from large, automated plants run by multinationals to smaller, semi-automated facilities operated by local firms.
The production process is heavily influenced by the availability and cost of key raw materials, primarily isocyanates and polyols, which are petrochemical derivatives. While some basic polyols may be produced regionally, Vietnam remains largely dependent on imports for high-quality isocyanates and specialized polyols, primarily from China, South Korea, Thailand, and the Middle East. This import dependency introduces an element of cost volatility and supply chain vulnerability, which domestic producers must manage through inventory strategies and supplier relationships.
Trade and Logistics
Vietnam’s trade in polyurethane sealants reflects its status as a developing industrial economy with a strong manufacturing base. The country operates as both a significant importer and a growing exporter, creating a complex trade flow. Imports consistently outstrip exports in value, indicating a reliance on foreign technology and high-specification products that are not yet produced domestically at scale or competitively. The import channel is crucial for supplementing domestic supply, especially for projects with stringent technical requirements.
The import landscape is dominated by a few key origins. China stands as the largest source, benefiting from geographical proximity, competitive pricing, and a comprehensive chemical industry. Other major supplying countries include South Korea, Japan, Thailand, and Germany, with each often specializing in different product tiers; for instance, German and Japanese imports are frequently associated with high-performance industrial grades, while Thai and Chinese imports cover a broader range, including standard construction sealants.
On the export front, Vietnam has been steadily increasing its shipments, primarily within the ASEAN region and to other neighboring markets. Exports often consist of standard-grade construction sealants and products for furniture assembly, where Vietnamese manufacturers have developed cost-competitive advantages. This export growth is supported by free trade agreements within ASEAN and demonstrates the increasing capability and quality recognition of local production. However, exports remain a smaller portion of total production compared to domestic sales.
Logistics and distribution networks are critical to market efficiency. For imports, major seaports such as Cat Lai (Ho Chi Minh City) and Hai Phong are the primary gateways, with customs clearance and quality inspection being key procedural nodes. Domestic distribution is multi-layered, involving a network of national distributors, regional wholesalers, and retail outlets (both specialized building material stores and large-format retail). For large project supply, manufacturers or their exclusive distributors often engage in direct sales to construction contractors or industrial OEMs, bypassing traditional channels.
Price Dynamics
Pricing in the Vietnamese polyurethane sealants market is influenced by a multifaceted set of factors, creating a dynamic and sometimes volatile environment. The single most significant determinant is the cost of raw materials, particularly isocyanates (like MDI and TDI) and polyols, which are tied to global petrochemical prices. Fluctuations in crude oil prices, supply disruptions in major production regions, and changes in trade policies for chemical intermediates can cause rapid and substantial shifts in input costs, which manufacturers must pass through the value chain.
Beyond raw material costs, pricing strategies vary significantly across market segments and competitor tiers. Multinational brands typically command a price premium of 20% to 50% over comparable local products, justified by perceived higher quality, technical support, brand assurance, and compliance with international standards. In the mid and economy segments, competition is fierce, with price being a primary purchase driver. Here, domestic manufacturers compete intensely with each other and with lower-cost imports, leading to narrower margins.
End-use sector dynamics also dictate price elasticity. In large, tender-based infrastructure projects, price is a critical component of bidding, but it is balanced against technical specifications and warranty requirements. In the industrial OEM sector, consistency, certification, and just-in-time delivery can be as important as price, allowing for more stable pricing agreements. Conversely, in the retail and DIY segment, consumers are highly price-sensitive, promoting promotional pricing and economy-sized packaging.
Currency exchange rate volatility adds another layer of complexity. Given the high dependency on imported raw materials and equipment, a depreciation of the Vietnamese Dong (VND) against the US Dollar or Chinese Yuan directly increases production costs for local manufacturers. Similarly, importers face higher landed costs for finished goods. This exchange rate risk is a constant factor in pricing strategies, inventory planning, and contract negotiations, particularly for long-duration projects.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive arena for polyurethane sealants in Vietnam is intensifying, marked by the coexistence of global giants and ambitious local contenders. The market structure can be segmented into three broad tiers. The first tier consists of the multinational corporations (MNCs) such as Sika, Henkel, 3M, and Arkema (Bostik), which possess full-range portfolios, strong R&D backing, and direct relationships with major multinational contractors and industrial OEMs operating in Vietnam.
The second tier includes other international players and the leading domestic manufacturers. Companies from South Korea, Japan, and Thailand have established strong footholds, often through local partnerships. Prominent Vietnamese firms have grown substantially, investing in brand building, production technology, and distribution networks. These players successfully compete for public projects, private developments, and industrial accounts where a balance of quality, price, and local service is paramount.
The third tier comprises numerous smaller domestic producers and trading companies that import and repackage sealants. This segment is highly fragmented and competes almost exclusively on price, serving the low-end construction market, rural areas, and small-scale workshops. While individually their market share is small, collectively they represent a significant volume, particularly in price-sensitive segments, and contribute to overall market price pressure.
Key competitive strategies observed in the market include:
- Product Differentiation & Innovation: Leaders invest in developing new formulations, such as low-VOC, fast-cure, or high-movement capability sealants, to create technical barriers and access premium applications.
- Vertical Integration & Backward Integration: Some larger players are investing in upstream raw material production or compounding facilities to secure supply and control costs.
- Distribution Network Expansion: Strengthening reach into secondary cities and provincial markets is a priority for both MNCs and local leaders to capture decentralized growth.
- Strategic Partnerships: Forming alliances with large construction conglomerates, real estate developers, or automotive OEMs to secure preferred supplier status and project pipelines.
Methodology and Data Notes
This report on the Vietnam Polyurethane Sealants Market is the product of a rigorous, multi-faceted research methodology designed to ensure accuracy, depth, and strategic relevance. The foundational approach integrates primary and secondary research, quantitative data modeling, and expert validation to construct a comprehensive market view. All analysis is anchored in verifiable data sources and structured analytical frameworks, providing a reliable basis for strategic decision-making.
Primary research formed a critical pillar of the methodology, involving in-depth interviews and surveys with key industry participants. This included structured discussions with executives from leading polyurethane sealant manufacturers (both multinational and domestic), major distributors and wholesalers, procurement managers from construction and industrial firms, and industry association representatives. These interviews provided firsthand insights into market dynamics, competitive strategies, pricing trends, supply chain challenges, and future expectations that cannot be gleaned from desk research alone.
Secondary research encompassed an exhaustive review of publicly available and proprietary information sources. This included analysis of company annual reports, financial statements, and press releases; government publications from Vietnam’s General Statistics Office (GSO), Ministry of Construction, and Ministry of Industry and Trade; international trade databases detailing import and export flows; technical publications and industry journals; and relevant news and macroeconomic reports. This data was systematically collected, cross-referenced, and synthesized to build a consistent market dataset.
The collected quantitative and qualitative data was then processed through IndexBox’s proprietary market modeling tools. This involved triangulation of data points from different sources, demand-supply gap analysis, and the application of statistical techniques to estimate market size, segment shares, and growth trends. The forecast to 2035 is based on a combination of time-series analysis, correlation with macroeconomic indicators (GDP, construction growth, industrial output), and scenario-based modeling that considers identified growth drivers and potential constraints. It is crucial to note that while the report provides a detailed forecast framework, it does not invent new absolute figures beyond the scope of its 2026 base year analysis.
Outlook and Implications
The trajectory of the Vietnamese polyurethane sealants market from 2026 towards 2035 is poised for continued expansion, albeit within a context of increasing complexity and evolving challenges. The fundamental demand drivers—urbanization, infrastructure development, and industrial growth—are expected to remain potent, supporting a positive long-term growth curve. However, the nature of this growth will likely shift from purely volume-driven to increasingly value-driven, influenced by technological advancement, sustainability mandates, and intensifying competition.
Several key trends are anticipated to shape the market landscape over the forecast period. The push towards sustainable construction will accelerate, driving demand for low-VOC, solvent-free, and bio-based polyurethane sealants. This will favor companies with strong R&D capabilities and the ability to navigate evolving green certification schemes. Concurrently, digitalization will impact the market through e-commerce channels for standard products, digital tools for specification and technical support, and data-driven supply chain management, enhancing efficiency and customer engagement.
The competitive environment is expected to consolidate further, particularly in the mid-tier segment. Leading domestic manufacturers may seek to acquire smaller players to gain scale, distribution, and product line breadth. Multinational corporations might deepen their local manufacturing footprint to improve cost competitiveness and better serve the market. The competitive battleground will extend beyond product features to encompass total cost of ownership, technical service, sustainability credentials, and supply chain reliability.
For stakeholders—including manufacturers, distributors, investors, and end-users—the implications are significant. Manufacturers must prioritize innovation aligned with sustainability trends and invest in supply chain resilience to mitigate raw material volatility. Distributors need to enhance their technical advisory capabilities and logistics networks to serve a more demanding customer base. Investors should look for companies with strong brands, integrated operations, and clear sustainability strategies. End-users, particularly large contractors and OEMs, will benefit from a wider range of advanced products but must also develop more sophisticated procurement strategies to balance performance, cost, and compliance in an increasingly complex market.
Source: IndexBox Platform