Water damage in your foundation undermines structural stability by allowing moisture to infiltrate concrete and masonry, leading to cracks, mold growth, and costly repairs. Homeowners who recognize early warning signs and implement proven prevention methods can safeguard their property value and indoor air quality. This guide explains the common causes of foundation water damage, how to spot symptoms early, key exterior and interior defenses, repair options and costs, long-term maintenance practices, advanced drainage systems, and monitoring techniques. By following these strategies, you’ll understand hydrostatic pressure, soil expansion, waterproofing solutions, sump pump selection, professional intervention thresholds, and seasonal inspection checklists to keep your home’s base dry and secure.
What Are the Common Causes of Water Damage in Foundations?
Water damage in foundations occurs when excess moisture exerts pressure on structural elements, corrodes reinforcement, and triggers long-term deterioration. Recognizing these causes empowers homeowners to target the root issues before cracks form and mold develops.

 How Does Hydrostatic Pressure Affect Your Foundation?
How Does Hydrostatic Pressure Affect Your Foundation?
Hydrostatic pressure builds when groundwater accumulates outside foundation walls, forcing water through pores and hairline fissures and causing wall bowing and seepage. As soil saturation rises after heavy rain, the increasing lateral force can crack a basement wall within days to weeks, depending on conditions. Understanding this pressure dynamic highlights why grading and drainage systems must direct water away from the foundation to relieve stress and prevent structural compromise.
Hydrostatic Pressure and Foundation Damage
Hydrostatic pressure, caused by groundwater accumulating around a foundation, can exert significant force, leading to cracks, leaks, and structural damage. This pressure is particularly problematic in areas with high rainfall or poor drainage, potentially causing walls to bow or even collapse over time.
This research highlights the importance of understanding hydrostatic pressure and its impact on foundation integrity.
What Role Do Expansive Soils and Poor Drainage Play in Foundation Damage?
Expansive soils, such as clay, swell when wet and shrink when dry, exerting cyclic stresses that lead to uneven settling and slab heave in concrete foundations. Poor site drainage compounds this issue by allowing water to pool against foundation walls, accelerating soil expansion and contraction cycles. Recognizing soil type and ensuring gutter downspouts discharge at least 5 to 10 feet from the house base prevents repeated soil movement that can crack footings.
Expansive Soils and Foundation Damage
Expansive soils, especially those with high clay content, can cause significant damage to foundations due to their tendency to swell when wet and shrink when dry. This cyclical movement can lead to cracks, uneven floors, and structural issues, making proper soil assessment and foundation design crucial.
This research supports the article’s discussion of expansive soils and their impact on foundation integrity.
Can Plumbing Leaks and Flooding Lead to Foundation Water Damage?
Yes, plumbing leaks beneath slab foundations or in crawl spaces introduce continuous moisture that compromises vapor barriers and corrodes metal supports. Flooding events can also saturate soil and masonry, leading to efflorescence and mold proliferation. Fixing hidden pipe leaks and installing backflow prevention valves stops moisture intrusion at the source and preserves foundation integrity.
What Are the Key Signs and Symptoms of Foundation Water Damage?
Foundation water damage reveals itself through a combination of visual cues and environmental changes that homeowners can monitor regularly. Early detection prevents small issues from escalating into major structural failures.
How to Identify Foundation Cracks and Bowing Walls Early?
Fine horizontal cracks near the middle of a basement wall indicate hydrostatic pressure pushing inward, while vertical hairline cracks often result from settling or shrinkage. Inspect walls quarterly with a flashlight, marking crack length and width to track progression. Addressing these cracks with appropriate sealants or wall anchors prevents bowing walls from advancing to structural failure.
What Are the Visible Signs of Mold and Efflorescence in Basements and Crawl Spaces?
Efflorescence appears as white mineral deposits on concrete surfaces when water evaporates and leaves salt crystals behind, while mold grows in dark, damp corners as black, green, or brown patches. Both indicate persistent moisture intrusion that undermines indoor air quality and can corrode structural materials. Cleaning affected areas and correcting moisture sources prevents health risks and masonry deterioration.
How Do Uneven Floors and Musty Smells Indicate Water Damage?
Uneven or sagging floor slabs often result from soil washout or heave beneath, while musty odors signal mold growth in hidden cavities. A moisture meter used along floor joints can confirm elevated relative humidity levels that support microbial colonies. Recognizing these subtle cues lets homeowners target crawl spaces and slabs for encapsulation and dehumidification before damage spreads.
How Can Homeowners Prevent Water Damage to Their Foundations?
Preventing foundation water damage involves managing exterior runoff, improving interior barriers, and installing mechanical safeguards that operate continuously. A multi-layered waterproofing system reduces risk and extends foundation life.
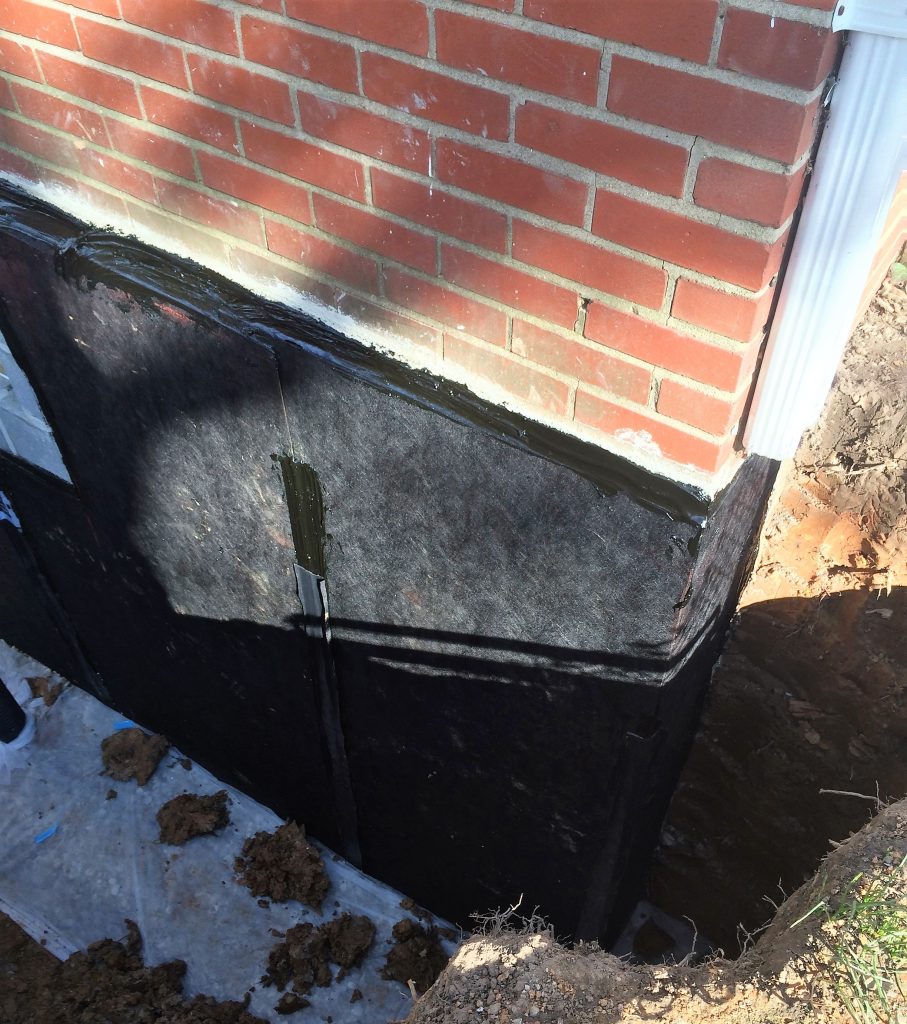
What Exterior Drainage Solutions Protect Foundations from Water Intrusion?
Effective exterior drainage relies on sloping soil away from the foundation, adding French or footing drains, and maintaining gutters and downspouts. A well-graded yard with a 2% to 5% slope directs rainwater away, while perforated pipe systems collect and redirect groundwater before it contacts the foundation wall. These measures relieve hydrostatic pressure and keep footing soil stable.
How Do Interior Waterproofing Methods Help Prevent Water Damage?
Interior waterproofing installs sealants, vapor barriers, and channel drains along the footing line to capture and redirect seepage to a sump pump system. Epoxy or polyurethane injections in foundation cracks provide a watertight barrier, and interior drainage channels beneath the slab intercept moisture before it reaches living areas. Combining these methods with exterior solutions ensures a comprehensive defense.
What Are the Benefits of Crawl Space Encapsulation and Dehumidification?
Crawl space encapsulation involves installing a heavy-duty vapor barrier on floor and wall surfaces, sealing vents, and insulating perimeter walls to create a conditioned cavity. Adding a dehumidifier maintains relative humidity below 60%, preventing mold growth, wood rot, and musty odors. This process supports indoor air quality, reduces structural decay, and protects insulation performance.
How Does Installing a Sump Pump System Reduce Water Risks?
A sump pump removes collected water from interior drain channels or a dedicated sump basin, actively lowering the groundwater level around the foundation. By discharging water away from the home, the pump mitigates hydrostatic pressure and prevents basement flooding during heavy precipitation. Choosing the right pump type ensures reliability and appropriate performance for specific foundation conditions.
What Types of Sump Pumps Are Best for Different Foundations?
| Pump Type | Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Submersible Pump | Deep sump pits in finished basements | Quiet operation and high pumping capacity |
| Pedestal Pump | Shallow pits in crawl spaces or garages | Easy maintenance and lower cost |
| Battery-Backup Pump | Homes prone to power outages | Uninterrupted operation during outages |
| Combination Pump | High-risk flood zones | Dual power source for maximum reliability |
Choosing a compatible pump configuration aligns water removal capacity with foundation drainage needs, ensuring continuous protection when storms strike.
When and How Should You Repair Foundation Water Damage?
Repairing foundation water damage requires selecting the right method based on crack severity, moisture patterns, and structural risk. Timely intervention prevents minor leaks from developing into extensive structural repairs.
What Foundation Crack Repair Methods Can Homeowners Do Themselves?
Homeowners can seal small cracks with injection kits using epoxy or polyurethane foam, which bonds to concrete and prevents water penetration. Applying masonry caulk along hairline fissures also restores watertight integrity. For larger cracks or bowing walls, professional wall anchors and carbon-fiber reinforcement deliver the necessary strength beyond DIY capability.
Foundation Crack Repair Methods
Effective methods for repairing foundation cracks include epoxy injection, which bonds concrete and creates a waterproof seal, and the use of hydraulic cement for larger cracks. For more severe issues, techniques like wall anchors and piers may be necessary.
This research supports the article’s discussion of foundation crack repair methods.
How Do Basement Waterproofing Techniques Differ: Interior vs. Exterior?
Exterior waterproofing applies waterproof coatings, drainage membranes, and footing drains to the foundation’s exterior face, providing the most robust barrier before water contacts the wall. Interior solutions use sealants, channel drains, and sump pump systems inside the basement to manage water after entry. Exterior methods require excavation but offer long-term protection, while interior techniques are less invasive and cost-effective for moderate seepage.
Basement Waterproofing Techniques
Basement waterproofing methods include interior sealants, exterior waterproofing, and drainage systems like sump pumps and French drains. Exterior waterproofing involves applying a waterproof membrane to the foundation’s exterior, while interior solutions manage water after it enters the basement.
This research provides further details on the various methods used to prevent water damage in basements.
When Is It Necessary to Hire a Foundation Repair Professional?
Engage a foundation repair specialist when cracks exceed 1/8-inch, walls begin to bow, or repeated moisture control measures fail. Licensed experts perform structural assessments, install helical piers or underpinning, and ensure compliance with building codes. Professional intervention safeguards against settlement, prevents future movement, and preserves long-term property value.
What Are the Typical Costs of Foundation Water Damage Repairs?
Repair expenses vary by method, damage extent, and region, ranging from simple crack sealing to full-scale waterproofing and underpinning. Knowing these cost brackets helps homeowners budget and prioritize interventions based on risk.
| Repair Scope | Average Cost Range | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Crack Injection | $500 – $1,500 | Epoxy/polyurethane sealing of minor fissures |
| Interior Drainage & Sump | $3,000 – $7,000 | Channel drains and pump system installation |
| Exterior Waterproofing | $7,000 – $15,000 | Excavation, membrane application, drainage setup |
| Underpinning & Structural | $10,000 – $25,000+ | Helical piers, footing stabilization, wall repair |
How Do Repair Costs Vary by Region and Damage Severity?
Repair expenses reflect local labor rates, climate factors, and soil conditions, with urban areas often 20–40% higher than rural regions. Severe bowing and advanced structural issues can double standard pricing, while simple crack sealing remains affordable across locations. Assessing regional benchmarks and obtaining multiple estimates ensures transparent pricing.
What Long-Term Maintenance Practices Help Protect Foundations From Water Damage?
Routine foundation care prevents water damage from resurfacing and extends the life of waterproofing investments. A proactive maintenance schedule addresses seasonal risks and environmental changes.
What Should a Seasonal Foundation Maintenance Checklist Include?
- Inspect and clear gutters, downspouts, and splash blocks
- Verify soil grading maintains 2% to 5% slope away from foundation
- Check sump pump operation and test battery backup systems
- Examine basement and crawl space for new cracks or efflorescence
- Monitor interior humidity and run dehumidifiers as needed
Seasonal Foundation Maintenance Checklist
A seasonal maintenance checklist should include inspecting and clearing gutters, verifying proper soil grading, checking sump pump operation, and monitoring for new cracks or efflorescence. Consistent maintenance helps preserve drainage performance and alerts homeowners to emerging issues.
This research provides a detailed checklist for maintaining a foundation.
How Does Water Damage Impact Home Value and Insurance Claims?
Foundation water damage reduces resale value by approximately 10–15% and can trigger insurance claim denials if maintenance neglect is proven. Documented waterproofing installations and repair receipts support insurance coverage and demonstrate due diligence. Maintaining a dry foundation enhances marketability and protects against unexpected claim disputes.
What Advanced Moisture Control Strategies Can Extend Foundation Life?
Beyond standard barriers, advanced strategies include installing smart sump systems with remote monitoring, integrating perimeter moisture sensors, and applying crystalline waterproofing admixtures in concrete. These solutions provide real-time alerts and self-sealing properties that respond to emerging leaks. Leveraging technology improves long-term reliability and reduces manual inspection frequency.
What Are the Best Drainage Systems to Prevent Foundation Water Damage?
Effective drainage systems divert excess water before it reaches your foundation, eliminating hydrostatic pressure and soil saturation risks. Selecting the correct system type depends on site conditions, soil type, and water volume.

 How Do French Drains and Footing Drains Work to Divert Water?
How Do French Drains and Footing Drains Work to Divert Water?
French drains use perforated pipes surrounded by gravel in trenches that collect subsurface water and channel it away from the foundation. Footing drains sit directly alongside the foundation footing, capturing water at its source and directing it into a sump basin or daylight outlet. Both systems relieve lateral water pressure and maintain stable soil moisture levels.
What Is Yard Grading and How Does It Protect Your Foundation?
Yard grading reshapes the landscape to create a consistent slope away from foundation walls, ensuring rainwater flows downhill rather than pooling. A properly graded yard reduces surface water infiltration by up to 90%, easing the burden on subsurface drainage components. Regular regrading after landscaping work preserves this protective slope.
How Do Perforated Pipes and Gravel Enhance Drainage Systems?
Perforated pipes allow groundwater to enter the pipe along its length, while surrounding gravel filters out sediment and slows water flow to prevent clogging. This combination maximizes water collection capacity and ensures long-term performance of French and footing drain installations. Proper backfill and filter fabric further extend system lifespan.
How Can Homeowners Monitor and Detect Foundation Water Damage Early?
Continuous monitoring of moisture indicators and professional inspections enable early action before small leaks become major structural issues. A proactive detection approach combines visual checks with instrumentation for thorough coverage.
What Are the Most Effective Signs to Watch for Regularly?
Key indicators include new wall cracks wider than 1/16 inch, shifting floor elevations, rising efflorescence lines, peeling paint, and persistent musty odors. Weekly or monthly visual inspections, especially after storms, ensure these signs are caught at their onset. Early recognition reduces repair scope and cost.
How Can Homeowners Use Moisture Meters and Inspections?
A handheld moisture meter measures relative humidity inside walls, floors, and crawl spaces, identifying hidden damp zones before visible damage appears. Scheduling infrared or thermal imaging inspections detects moisture behind finishes. Combining these tools with professional assessments provides comprehensive leak detection.
When Should You Schedule Professional Foundation Inspections?
Arrange professional inspections if DIY measures fail to stop recurring seepage, cracks exceed threshold widths, or you detect structural movement. Experts perform soil analysis, structural load evaluations, and recommend underpinning or drainage overhauls. Timely professional guidance prevents costly retrofits and ensures compliance with safety standards.
Foundations challenged by water infiltration demand a holistic approach that combines exterior grading, interior barriers, mechanical pumping, and vigilant monitoring. By understanding hydrostatic pressure, soil behavior, and the full spectrum of waterproofing and repair techniques, homeowners can maintain a dry, stable foundation that preserves property value, indoor air quality, and structural integrity. Implementing a seasonal maintenance routine, choosing the proper drainage systems, and knowing when to call professionals ensures that water damage remains a preventable threat rather than an inevitable expense. Consistent attention to these strategies will extend your foundation’s lifespan and safeguard your home for years to come.
Having started in 1990, we boast expert staff members with collective experience in the industry going strong for over 50 years. We promise our clients superior workmanship and quality in basement waterproofing and foundation repair at budget-friendly prices, capped by a fantastic client experience to ensure your ultimate satisfaction.
We are a local and family-owned business committed to providing top-notch basement waterproofing service and workmanship. We are also actively involved in several non-profit projects for the betterment of our community. In 2020 we celebrated our 30th Anniversary.